C++ finance course for beginners – part 1 – hello world
REQUIREMENTS:
– microsoft visual studio express 2012 (it’s free,older versions are similar. there are slight differences between microsoft and linux c++)
– some programming experience in another language
Course objectives:
-price various derivatives using c++ code
-use basic quantlib and boost functions useful in financial engineering
C++ ,Boost and Quantlib install
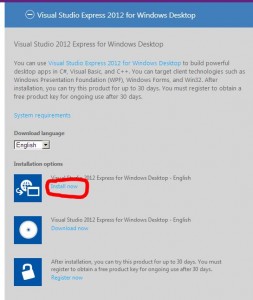
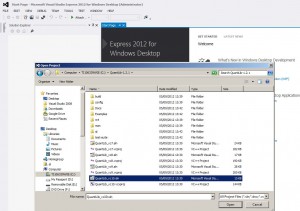
1)install visual studio 2012 express :
http://www.microsoft.com/visualstudio/eng/downloads#d-express-windows-desktop
2) install boost
– download latest version of boost from http://www.boost.org
– unpack it into drive C:
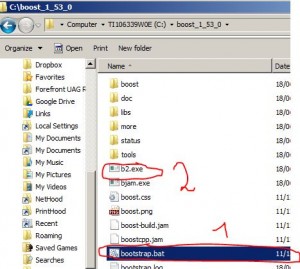
[so its unpacked into c:\boost_1_53_0 ]
– go to the dir c:\boost_1_53_0 and run bootstrap.bat
– run b2.exe
it will take few hours to build!
– go to dir c:\boost_1_53_0\stage
move whole dir “lib” to c:\boost_1_53_0\ so all built libraries are inside c:\boost_1_53_0\lib
3) install quantlib
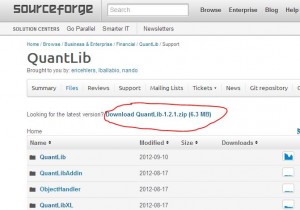
download quantlib
http://sourceforge.net/projects/quantlib/files/
unpack it to C:\
– open visual studio express for desktop
File->Open project -> QuantLib_vc10.sln
Choose “update” in the next dialog . it will convert files to visual studio 2012 format
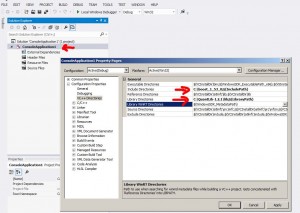
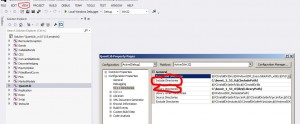
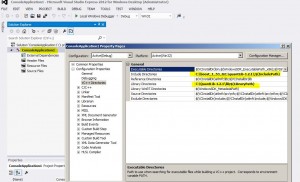
in the solution explorer window select QuantLib
press Shift-F4 (or Menu->View->Property pages)
change “include directories” variable to include path to boost
change “library directories” variable to include path to boost\lib
now delete all projects except QuantLib from the solution (click on every project in solution explorer and press “del”)
press F7 to build quantlib [or menu->build->build solution]
Hello world program
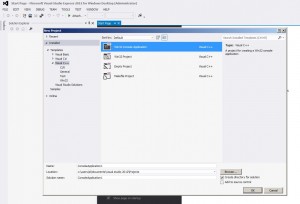
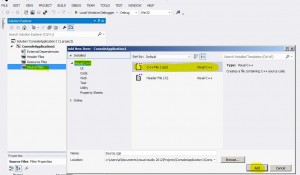
Menu -> New Project
choose Visual C++ -> Win32 Console Application
press OK->NEXT (do NOT press FINISH yet)
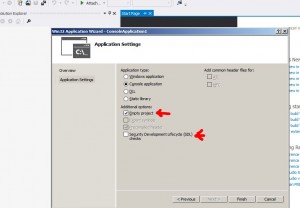
check “Empty Project”
uncheck “Security…” box
click Finish
right Click on ConsoleApplication1 anc change include and library directory to include QuantLib and boost directories:
right click on “Source Files” -> Add ->Add New Item
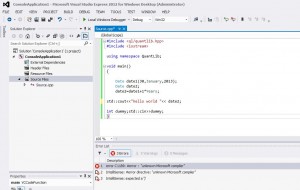
in the window copy paste following code:
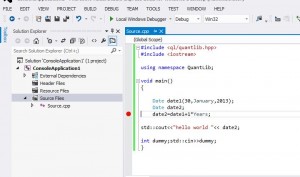
#include <ql/quantlib.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace QuantLib;
void main()
{
Date date1(30,January,2013);
Date date2;
date2=date1+1*Years;
std::cout<<date2;
int dummy;std::cin>>dummy;
}
press F7 to compile
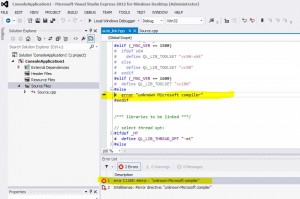
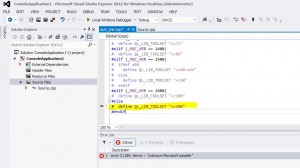
double click on error :
and change the following line :
# error "unknown Microsoft compiler"
by
# define QL_LIB_TOOLSET "vc100"
so it looks like that:
press F7 to build project and F5 to run
quick explanation of the code:
#include <ql/quantlib.hpp> #include <iostream>
these lines just insert files named quantlib.hpp and iostream into your source file
quantlib.hpp is needed to have quantlib functions and definitions (Date object)
and iostream is used to write to output console
using namespace QuantLib;
without this line you’d had to write “QuantLib::” before every quantlib object
void main()
{
Date date1(30,January,2013);
Date date2;
date2=date1+1*Years;
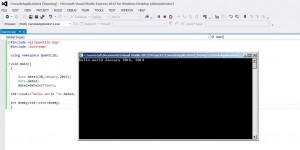
std::cout<<date2;
int dummy;std::cin>>dummy;
}
these lines define main function
in c++ when console program starts it automatically start executing the function main()
Date date1(30,January,2013); Date date2;
here we define two QuantLib objects(variables) date1 and date2 and assign a value for the first variable
date2=date1+1*Years; std::cout<<date2;
here we assign value for date2 to be 1 year from date1
and std::cout part prints the result to console
int dummy;std::cin>>dummy;
this is needed to pause the screen
debugging C++ program
to debug program left click where the red dot appears and press F5
the program will start debug and you can hover cursor over the variable to see it's value
as you can see date1 will show some long number instead of date .It's because internally quantlib uses Excel format for dates .
press F10 to execute instructions one by one of F5 again to continue program until next break point
![[<<] PriceDerivatives blog](http://www.pricederivatives.com/en/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/cropped-pricederivatives-blog-logo-Copy3.png)