Here we show simplest method called current net exposure
for more elaborated Monte-Carlo method using python see CVA with monte carlo calculation
for online interest rate swaps and OTC derivatives valuation with CVA see Derivatives accounting calculators
CVA calculation online with current net exposure method online
derivatives CVA calculation example:
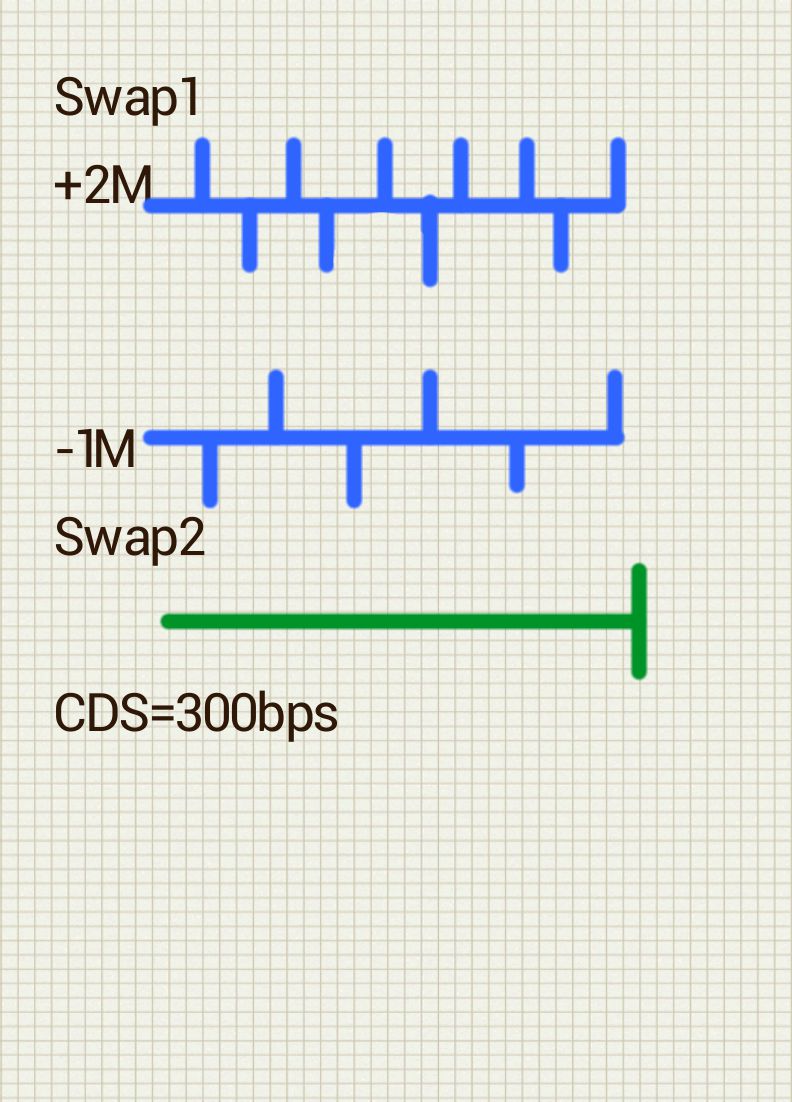
lets say we have derivatives portfolio with the same counterparty which consist of 2 amortizing swaps
one approximate method for would be to calculate Net exposure at valuation time
lets say swap1 worth today 2M$
swap2 worth -1M$
if there’s a netting agreement then total today’s exposure is (1-R)*(2M-1M) = (1-R)*1M $
R is recovery normally supposed to be at 40%
then CVA would be price to hedge this exposure with CDS (fixed leg of CDS)
lets say counterparty Credit Defualt Swap spread is flat 300 pb (3%)
then the cost of this hedge would be approximately
CVA=3% * (maturity in years) * (1-R) *1M $
if we want to improve the quality of this approximation we could take average exposure of swaps until maturity (at maturity exposure to swap is 0) which equals exposure today /2
so final formula would be
CVA=0.5*3% * (maturity in years) * (1-R) *1M $
in case that two swaps have different maturity then we would have to weight the exposure by maturity factor of each instrument
if total exposure is negative with this method CVA=0 and we would have to take own CDS spread to calculate DVA (debit valuation adjustment)
example cva calculation in Excel (you can edit cells)
FAS 157 require derivatives CVA to be calculated for fair value of derivatives, as well as basel 3 for banks
Derivatives CVA calculation example excel
to calculate value of annuity properly we can use quantlib addin from http://quantlib.org/quantlibxl/
1) first install quantlib addin at http://quantlib.org/quantlibxl/ -> download
2) open file at QuantLibXL\xll\QuantLibXL-vc90-mt-s-1_2_0.xll
3) open spreadsheet ctrl-alt-f9 to recalculate all
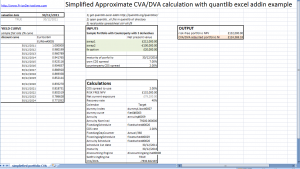
Here we calculate simplified derivatives CVA/DVA for a portfolio of 3 OTC derivatives with the same counterparty
if net current exposure is negative then we’ll have only DVA and we’ll use institution’s own CDS spread, else we’ll have only CVA and we’ll need to apply counterparty CDS spreads (both found on bloomberg or reuters terminals).
In this example we use sample flat curve for discounting. For proper use we’ll need to paste real curve for desired valuation date (also found on bloomberg or reuters)
the standard recovery of 40% is used.
to calculate annuity we’ll calculate swap value with 0 floating leg using quantlib addin functions for swap.
download excel:
cva calculation excel
references:
Stein_H_FeSeminar_Sp12.pdf
investopedia
credit value adjustement
![[<<] PriceDerivatives blog](https://www.pricederivatives.com/en/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/cropped-pricederivatives-blog-logo-Copy3.png)